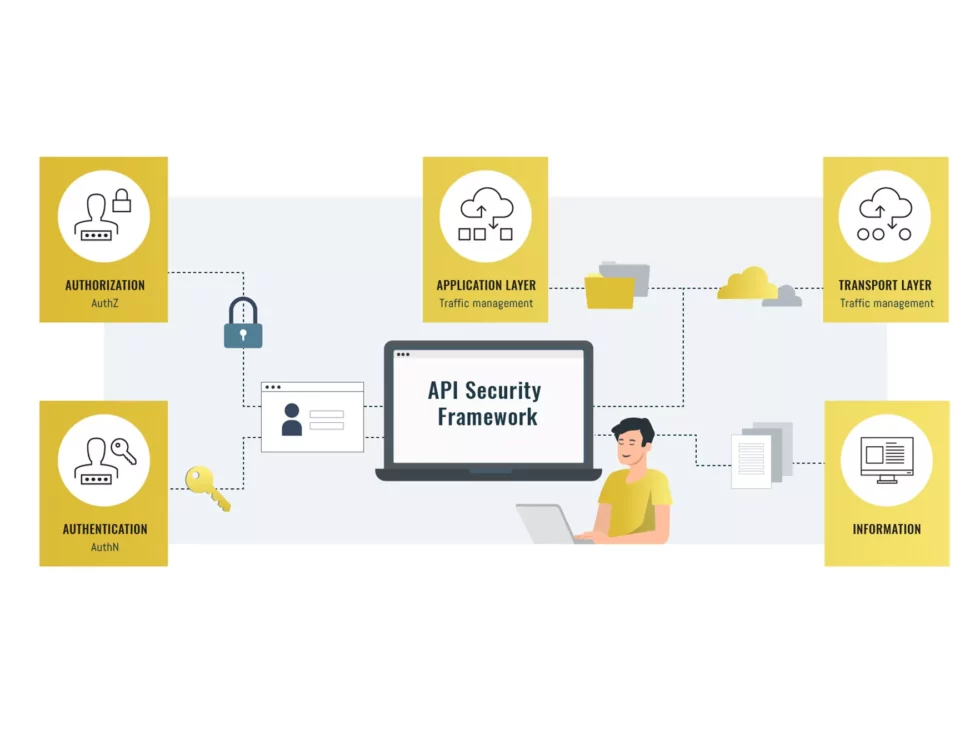
The last aspect that we are going to cover in this blog is about authentication factors. Let’s say that you have an API that is secured and only authorized API consumers are granted access. In this case, it is very important that you can trust whether your API consumer is who he says he is. Authentication is the process of proving identity (verifying whether you are what you say you are). Usually, authentication is done by a username and password, although there are other various ways to be authenticated.
Authentication factors determine the many different elements the system uses to verify identity. Based on the security level, authentication factors can vary from one of the following:
- Single-Factor Authentication: This is the simplest form of authentication method which requires 1-factor (I.e. username/password, client-certs, JWT token, …) to prove identity. Access to the API can be requested using only 1 factor to verify your identity. For example, only requiring a password against a username would be a way to verify a login credential using single-factor authentication.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: This authentication requires a two (or more)- step verification process to prove identity and request access to the API, preferably from different categories (Username/password, “Its me”, …). It’s a good practice to utilize factors that are independent of each other in order to eliminate any data exposure. This makes it that much harder for hackers to steal valuable and personal data.
When an API must be secured, single-factor authentication can be seen as the minimal requirement. However, this might not be enough when you identify that a higher (more than default) security-level must be applied. Weak or stolen user credentials are hackers’ weapon of choice. Password theft is constantly evolving as hackers employ methods like key-logging, phishing, and pharming. Introducing multi-factor authentication solves this, but also adds complexity. Therefore, you should always evaluate if your API requires multi-factor authentication or single-factor authentication is sufficient.

![[RECAP] API Community Belgium: Online Lunch Meetup: Insights & Highlights](https://we-archers.sitesoft.be/app/uploads/2025/10/RECAP-API-Community-Belgium-–-Online-Lunch-Meetup-Insights-Highlights.webp)
